Copyright © 2024 roStudio.in
Micro Frontend Architecture : React JS
Breaking down monolithic frontend applications into smaller, independent, and modular parts.
Title: Exploring Micro Frontend Architecture in React JS: A Modular Approach for Scalable Web Development
Introduction: The world of web development is constantly evolving, and with the rise of complex and feature-rich applications, the need for scalable and maintainable architectures has become crucial. One such architectural approach gaining popularity is Micro Frontend Architecture. In this article, we will delve into the concept of Micro Frontends and how they can be implemented in React JS, the widely used JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
Understanding Micro Frontend Architecture: Micro Frontend Architecture is an architectural pattern that extends the principles of microservices to the frontend development world. It involves breaking down a large monolithic frontend application into smaller, more manageable and independent frontend modules. Each module, or micro frontend, is responsible for a specific feature or functionality of the application.
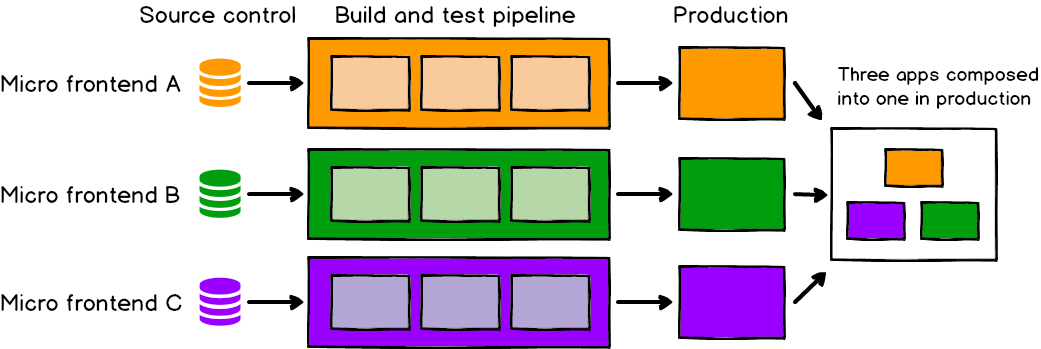
Benefits of Micro Frontend Architecture: Modular Development:
- Modular Development: Micro Frontends enable teams to work independently on different parts of an application. This promotes parallel development and allows teams to iterate quickly, reducing dependencies and bottlenecks.
- Scalability: With Micro Frontends, it becomes easier to scale an application by adding or removing modules as needed. This flexibility enables teams to focus on specific areas without impacting the entire application.
- Technology Agnosticism: Micro Frontend Architecture allows teams to choose the best technology stack for their specific module. This means different modules within an application can be built using different frameworks or libraries, such as React JS, Angular, or Vue.js, depending on the requirements and expertise of the team.
- Improved User Experience: By breaking down the frontend into smaller, focused modules, Micro Frontend Architecture enables faster loading times and reduces the impact of failures. Users can benefit from a seamless experience as changes to one module won't affect the entire application.
Implementing Micro Frontend Architecture in React JS: To implement Micro Frontends in React JS, we can leverage a few key techniques and tools. Here's an example scenario illustrating how this can be done:
Consider an e-commerce application consisting of three main features: product listing, shopping cart, and user profile.
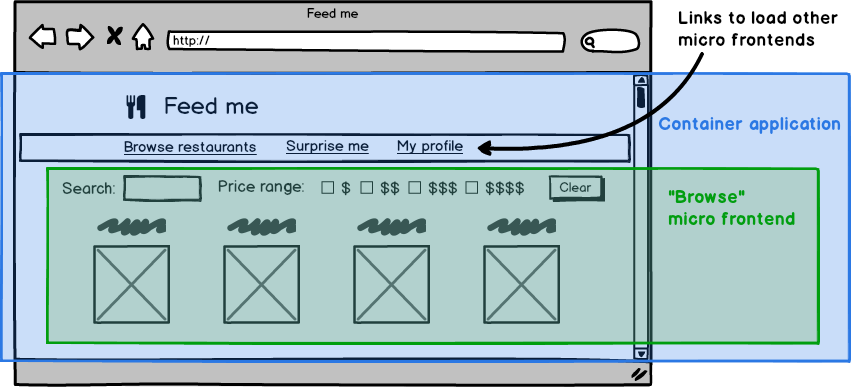
MFE Working Process
- Create Individual React Applications: Develop each feature as a separate React application, with its own set of components, views, and logic.
- Define Communication Channels: Establish communication channels between the micro frontends. This can be done using various techniques like events, shared state management libraries (e.g., Redux), or APIs.
- Container Application: Build a container application that acts as the shell for the micro frontends. The container application is responsible for loading and rendering the individual micro frontends based on the user's interactions.
- Routing and Navigation: Implement routing and navigation within the container application to handle the different micro frontends' views. This can be achieved using popular libraries like React Router.
- Routing and Navigation: Implement routing and navigation within the container application to handle the different micro frontends' views. This can be achieved using popular libraries like React Router.
- Deploy and Scale Independently: Each micro frontend can be deployed independently, allowing teams to update and scale their modules without affecting the entire application. This promotes faster releases and reduces the risks associated with deploying large monolithic applications.
In our webpack.config.js we introduce the ModuleFederationPlugin: Add the following code to the plugins.
// host-app/webpack.config.js
const ModuleFederationPlugin = require("webpack/lib/container/ModuleFederationPlugin");
const { dependencies } = require("./package.json");
module.exports = {
//...
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: "Host",
remotes: {
Remote: /`Remote@http://localhost:4000/moduleEntry.js/`,
},
shared: {
...dependencies,
react: {
singleton: true,
requiredVersion: dependencies["react"],
},
"react-dom": {
singleton: true,
requiredVersion: dependencies["react-dom"],
},
},
}),
],
};For Remote App Let’s start with the webpack configuration file. As we have configured it host-app, we have some knowledge of Module Federation:
const ModuleFederationPlugin = require("webpack/lib/container/ModuleFederationPlugin");
const { dependencies } = require("./package.json");
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: "Remote",
filename: "moduleEntry.js",
exposes: {
"./App": "./src/App",
"./Button": "./src/Button",
},
shared: {
...dependencies,
react: {
singleton: true,
requiredVersion: dependencies["react"],
},
"react-dom": {
singleton: true,
requiredVersion: dependencies["react-dom"],
},
},
}),Conclusion: Micro Frontend Architecture offers a modular and scalable approach to building complex web applications. By breaking down a frontend application into smaller, independent modules, teams can work in parallel, choose the most suitable technology stack for their module, and improve the overall user experience. React JS, with its component-based architecture and ecosystem of tools, is well-suited for implementing Micro Frontend Architecture. Embracing this approach can help teams build and maintain large-scale applications more effectively, enhancing productivity and flexibility in the development process.

